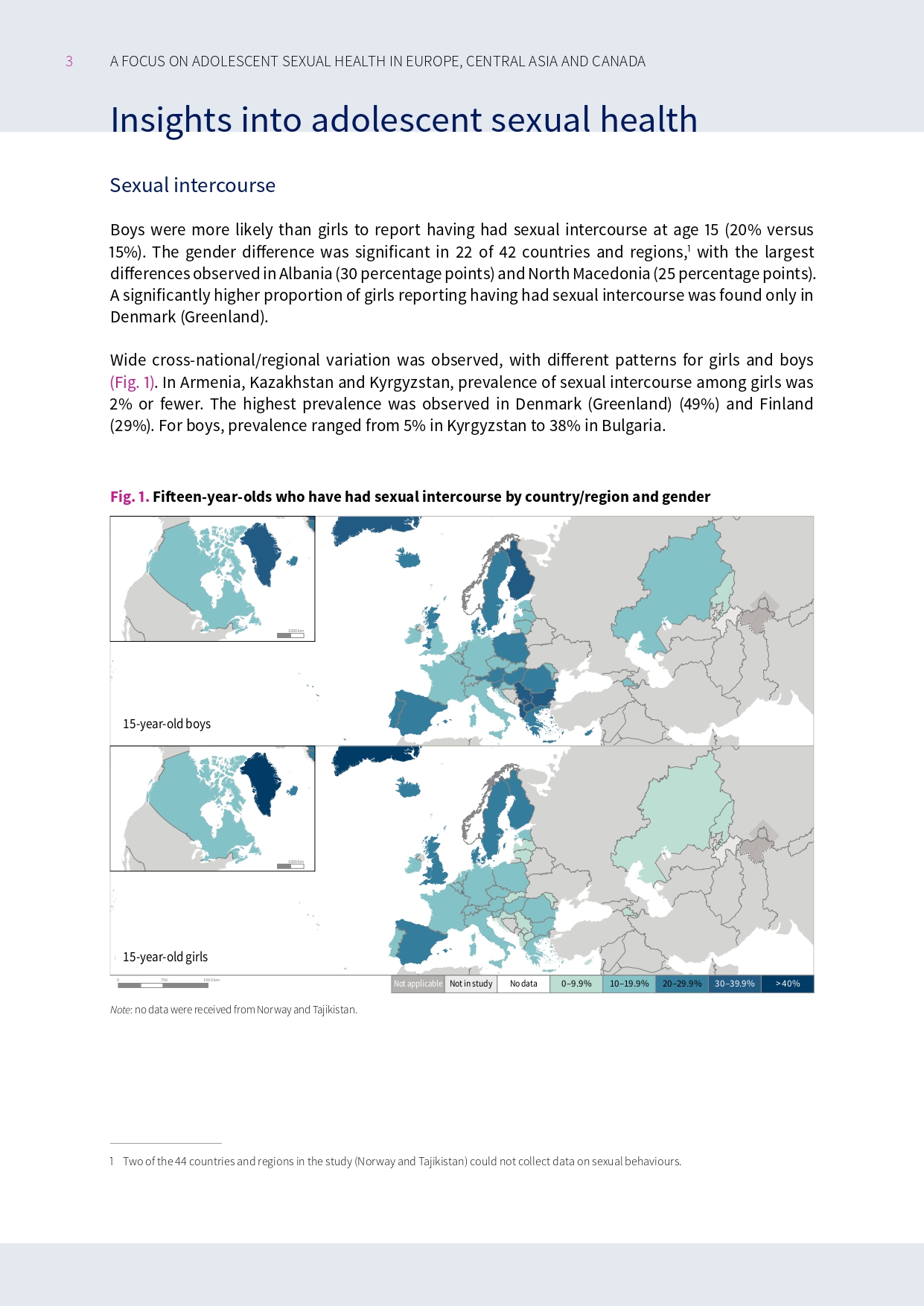

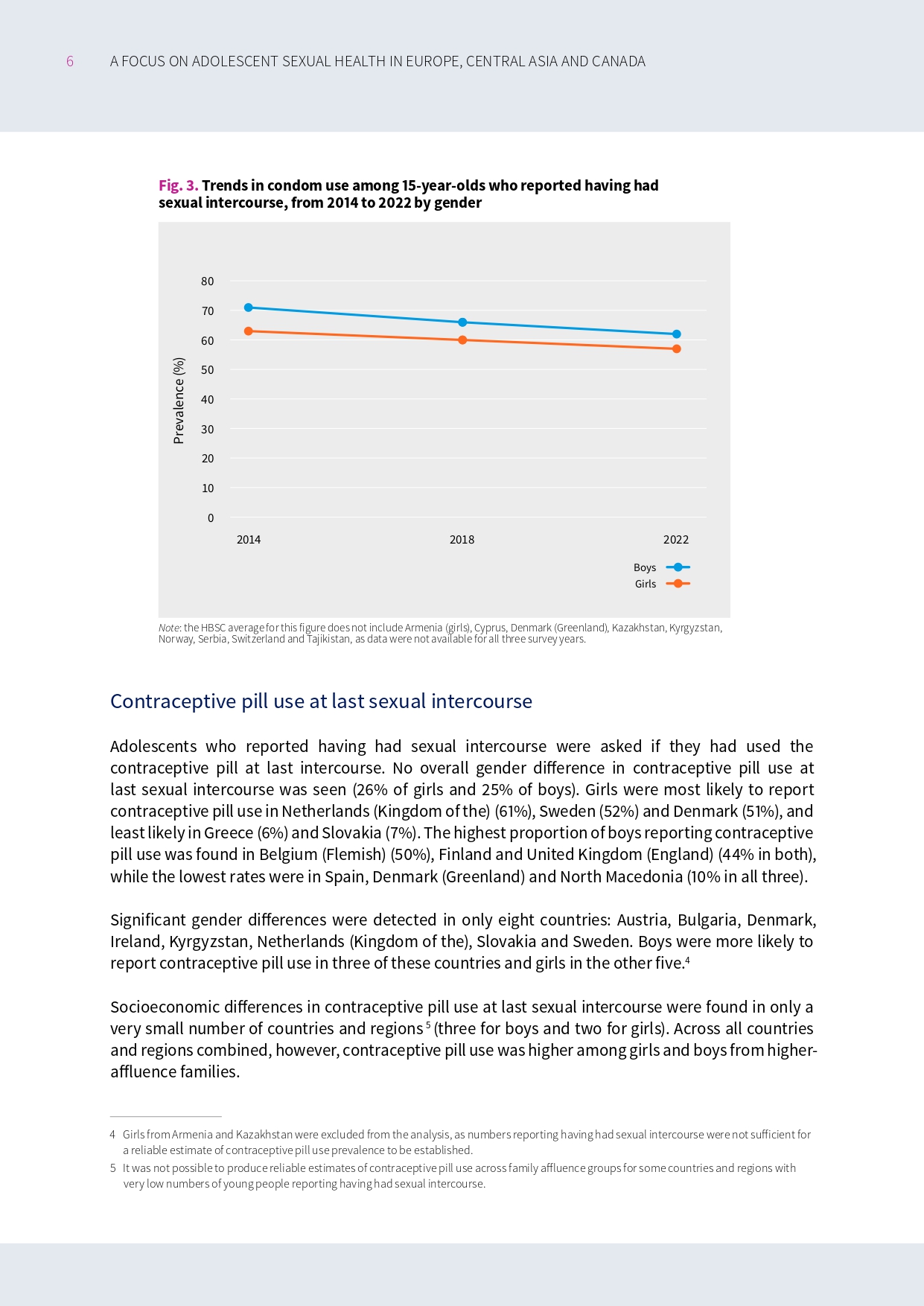

Our latest international report
This report from the 2021/2022 HBSC survey reveals concerning trends in adolescent sexual health, including a decline in condom use and high rates of unprotected sex. The findings highlight significant variations across countries and socioeconomic groups, emphasising the urgent need for comprehensive sexuality education and youth-friendly health services to support adolescent well-being.
The WHO Regional Office for Europe has today published a new report from the HBSC study, revealing concerning trends in adolescent sexual health.

A newly released fact sheet from the HBSC team in the Netherlands presents a nuanced picture of youth well-being. The findings reveal critical shifts in mental health, substance use, school experiences, and social media use—offering crucial insights to guide the support of young people throughout the Netherlands.

The Italian HBSC team has released a comprehensive report on digital technology use among adolescents, providing crucial insights into the patterns and potential risks associated with social media use and gaming habits.
 Other players are visible in the background." width="1080" height="675" />
Other players are visible in the background." width="1080" height="675" />
The report highlights unhealthy eating habits, rising rates of overweight and obesity, and low levels of physical activity among young people, all of which are significant risk factors for a range of non-communicable diseases including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes and cancer.

A newly released report from the Health Behaviour in School-aged Children (HBSC) team in Ireland paints a complex picture of youth well-being. The findings, published by the team at the University of Galway, reveal a mix of encouraging trends and areas of deepening concern.

A comprehensive analysis of the latest HBSC study data reveals significant insights into adolescent substance use patterns across Europe, Central Asia, and Canada. Published by WHO/Europe, the new report highlights concerning trends that demand attention and targeted preventive action.

The latest report from the Health Behaviour in School-aged Children (HBSC) study, published today by the WHO Regional Office for Europe, reveals critical insights into the prevalence and impact of peer violence and bullying among adolescents.

The EnCLASS survey, a joint initiative by the ESPAD and the HBSC study in France, offers a comprehensive analysis of substance use among French adolescents. Conducted between March and June of 2022, the survey included over 9,500 students from middle and high schools, providing valuable insights into the evolving patterns of alcohol, tobacco, and cannabis use.

Recent research from the HBSC network has brought to light a pivotal aspect of adolescent health – the role of spirituality. The new publication, titled "Establishing spirituality as an intermediary determinant of health among 42,843 children from eight countries," examines the concept of spirituality through a unique lens, revealing its profound influence on the mental health of children aged 11 to 15 years.

The HBSC study plays a key role at the ongoing Excellence in Pediatrics 2023 Conference, with Jo Inchley (International Coordinator) leading as co-chair and keynote speaker. The conference focuses on crucial adolescent health issues, and includes important updates from HBSC members on adolescent substance use and mental health.

The latest results from the 2021/22 HBSC study in England present a concerning landscape of adolescent health. Notably, the study reveals significant declines in both mental and physical health among young people, with disparities intensified by gender, age, and socio-economic status.

The recently published national report from HBSC Finland provides a detailed view of the health and well-being of Finnish 5th, 7th, and 9th graders in 2022. It reveals that while a majority of schoolchildren feel their health and mental well-being are good, notable concerns persist.

New results from the HBSC study’s 2021/22 international survey, reveal a worrying picture for adolescent mental health, with girls reporting worse outcomes than boys across all measures of mental health and well-being.

The Health Behaviour in School-aged Children (HBSC) study's Physical Activity Focus Group (PAFG) is delighted to announce a groundbreaking partnership with the Active Healthy Kids Global Alliance (AHKGA).

The latest HBSC 2021/2022 survey on Cyprus adolescents unveils a worrying rise in risky behaviours and mental health issues. Key concerns include increased e-cigarette and cannabis use, declining physical activity, and amplified mental health challenges.

The findings expose the COVID-19 pandemic's disproportionate effects on children and adolescents. Notably, the data underscores a more severe impact on those from lower socioeconomic backgrounds and those experiencing long-term school closures, as well as those lacking crucial social support systems.

New insights into Scottish adolescents' health and lifestyle trends were unveiled in HBSC Scotland's latest national report, published today at an event in Edinburgh.

The 2021/22 Health Behaviour in School-aged Children (HBSC) survey results in Sweden reveal concerning trends among the nation's 11, 13, and 15-year-olds, including declining school satisfaction, rising alcohol and snuff use, decreased condom use, and increasing health complaints.

Slovenian adolescents from lower-income households faced significant barriers to homeschooling in 2020, reveals the latest results from the Health Behaviour in School-aged Children (HBSC) study. These adolescents also experienced greater feelings of loneliness than those from more affluent families.

Among 15-year-old girls in Finland, 1 in 5 reported feeling low about their everyday life in 2022, according to the latest Health Behaviour in School-aged Children study results.

The latest results from the Estonian HBSC study reveal alarming mental health trends and suggest serious health consequences from the COVID-19 pandemic.

In Kazakhstan, urban and rural children experienced the COVID-19 crisis differently, reveals the latest Health Behaviour in School-aged Children study.

The first HBSC study in Kyrgyzstan shines a light on the health, well-being and social contexts of the nation’s youth, with worrying results for mental health.

New data from the HBSC (Health Behaviour in School-aged Children) study conducted by the Italian National Institute of Health reveals both positive and negative impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on Italian adolescents.
Tobacco, alcohol, and cannabis use have fallen among French adolescents in the last decade, particularly between 2018 and 2021, following the COVID-19 outbreak.

The 2021/22 Health Behaviour in School-aged Children (HBSC) study in Portugal shows a concerning decline in Portuguese adolescents' mental health and well-being compared to the 2018 HBSC survey.

A new report from the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), ‘Starting unequal: How’s life for disadvantaged children?‘, looks at the well-being of children from socially and economically disadvantaged backgrounds.

A report from the HBSC study reveals a troubling decline in the mental health of Dutch teenagers between 2017 and 2021, with girls being disproportionately affected. The report suggests that the COVID-19 pandemic has significantly contributed to the decline in mental health among teenagers, particularly girls.

Adolescents from unequal backgrounds are more likely to report a problematic use of Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp and other social media, according to new research using data from the 2017/18 Health Behaviour in School-aged Children (HBSC) study.
 Public release of 2017-18 data - October 2022" width="1080" height="675" />
Public release of 2017-18 data - October 2022" width="1080" height="675" />
The international file, including all mandatory variables for all regions and countries that took part in the 2017/18 HBSC survey, will be available via Open Access from October 2022.
Our primary goal in launching this new website is to provide visitors with a responsive, user-friendly experience that offers easy access to key information about the study and materials such as reports and other publications.

The new WHO European Regional Obesity Report 2022 reveals that almost two-thirds of adults and 1 in 3 children in the WHO European Region live with overweight or obesity, and these rates are growing.
Health Behaviour in School-aged Children (HBSC) is a WHO collaborative cross-national study of adolescent health and well-being. Founded in 1982, the survey is undertaken every four years using a self-report questionnaire. HBSC uses findings at national, regional and international levels to:
HBSC focuses on understanding young people’s health in their social context – at home, school, and with family and friends. It aims to improve understanding of how these factors, individually and collectively, influence young people’s health throughout adolescence.
The adolescent years are a critical transitional period within the life course during which rapid physical, emotional, cognitive, and social development occurs. These years mark a period of increased autonomy during which health-related behaviours develop and independent decision-making may influence their current and future health.
Behaviours established during this transition period can continue into adulthood, affecting issues such as mental health, substance use, physical activity levels and diet, and longer-term health outcomes. Exposure to alcohol or tobacco use, physical inactivity, unprotected sex or violence, presents risks not only to adolescents’ current health and well-being but also their future health.
The adolescent years, therefore, provide a critical opportunity for prevention and intervention to support young people’s healthy growth and development, promote future health and well-being in adulthood, and, as such, underpin the health of the next generation.
Data are collected in all participating countries and regions through school-based surveys using a standard methodology detailed in the HBSC international study protocol. Each country or region uses cluster sampling to select a proportion of young people aged 11, 13 and 15, ensuring that the sample is representative of all in the age range. Around 1500 students in each HBSC country or region are selected from each age group. Around 280,000 young people took part in the 2021/22 survey.